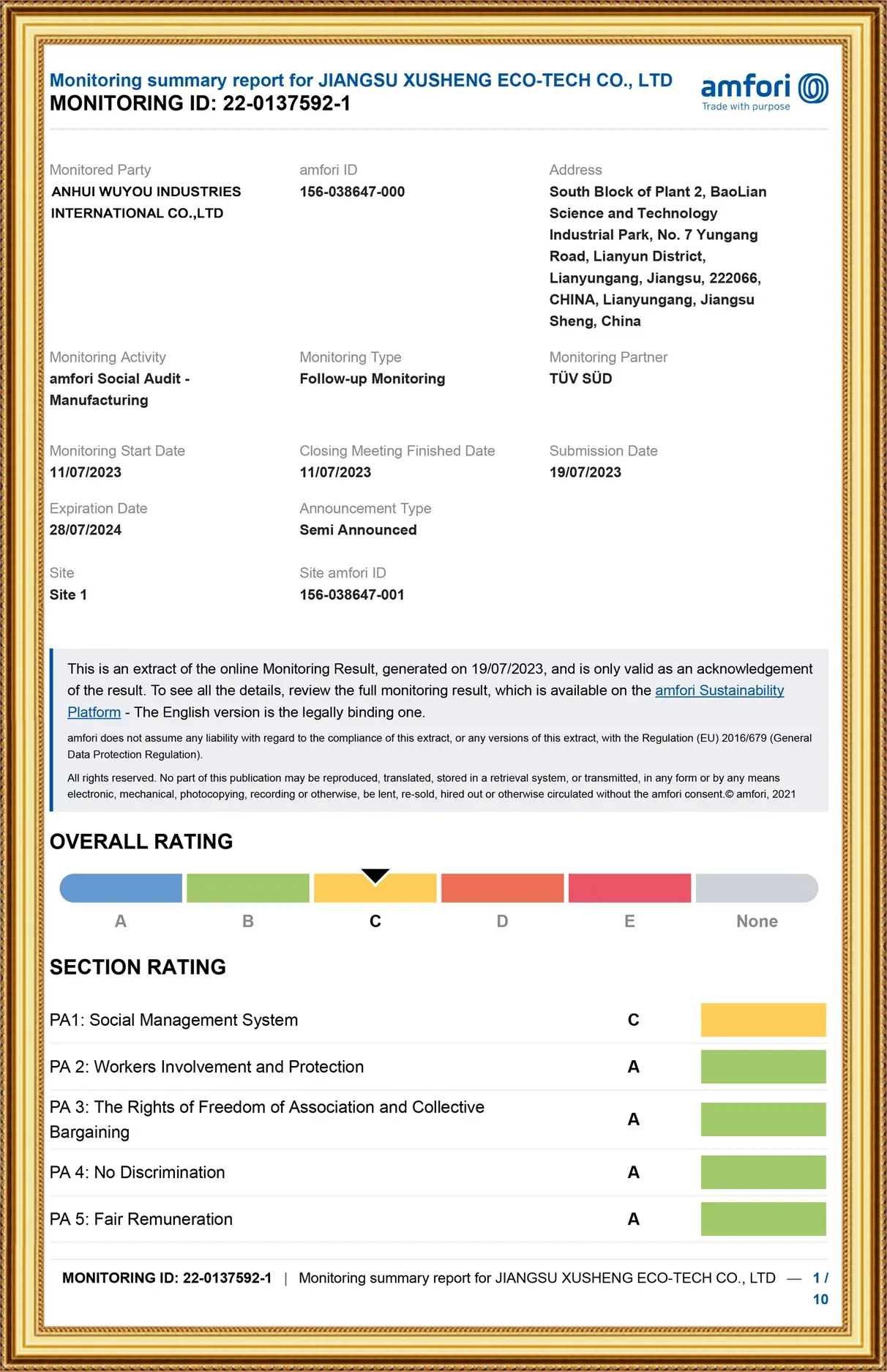
Company Overview
Anhui Wuyou Industries International Co., Ltd. is a high-tech environmental protection enterprise dedicated to the R&D and production of fully biodegradable tableware. With over 5 years of expertise in the biodegradable packaging industry, our products have gained global recognition, serving 100+ international clients. We provide eco-friendly, plastic-alternative solutions for industries such as catering, retail, food, and pharmaceuticals. Driven by innovation and sustainability, we remain at the forefront of the global green packaging revolution.
Our Mission
Eliminate White Pollution, Protect Our Planet!
We believe environmental responsibility is not an option but a duty. By developing 100% biodegradable packaging, we aim to reduce the harm caused by traditional plastics and accelerate the global transition to a circular economy. From raw material sourcing to production, design, and end-use, we uphold a “zero-pollution” commitment, empowering clients to achieve sustainable development goals.
Our Materials
Natural Ingredients: Sourced from Nature, Returned to Nature.
Sugarcane Bagasse Fiber: Repurposed from agricultural waste, transforming sugarcane residue into durable, eco-friendly products.
Wood Pulp-Based Materials: Food-grade options available to meet diverse needs.
Join the Green Revolution
Choosing Anhui Wuyou means investing in quality products and planetary stewardship.
Contact Us Today for custom solutions, free samples, or raw material partnerships. Together, let’s build a sustainable future!

Raw Materials
Our tenet is "quality first, customer first", and we aim to serve customers with high-quality products.
What is Sugarcane Fiber and Bagasse?
Products made from bagasse are considered sustainable because they reduce reliance on fossil fuels and non-renewable resources.
Bagasse, the fibrous byproduct of sugarcane processing, is widely used for food packaging, paper production, and bioenergy. Molded into plates, cups, and containers, it serves as a sustainable alternative in the food industry due to its compostable nature.
Additionally, bagasse is utilized in manufacturing paper and cardboard, while its high-energy content makes it suitable for generating bioenergy in processing plants. With growing concerns over plastic waste, bagasse's compostability and eco-friendly appeal have made it a popular choice for disposable tableware and other sustainable products.
How is Sugarcane Fiber (Bagasse) Produced?
The production process of sugarcane bagasse starts with the harvest of sugarcane and mainly includes the following steps:
Planting and Growing Sugarcane
Sugarcane is a crop widely grown in tropical and subtropical regions and thrives in warm, moist, well-drained soil. The growing period of sugarcane lasts from 12 to 18 months, and the best harvest time is usually the dry season to ensure that the sugar content in the sugarcane stem reaches its peak.
Harvesting Method
Harvesting By Hand
Use a machete or sickle to cut down the cane root by root. This method is suitable for areas with complex terrain or areas where mechanical operations are not suitable.
Mechanical Harvesting
Mechanized operations using specialized sugarcane harvesters can significantly increase efficiency and reduce labor costs.
During the harvesting process, the leaves and top immature parts of the sugarcane are removed, leaving only the stems that can be squeezed for juice.
Transportation and Processing
Transportation
After harvesting, sugarcane needs to be quickly transported to the sugar factory to reduce the natural loss of sugar in the sugarcane stems.
Processing
In sugar mills, sugarcane stems are crushed to extract their juice.
The extracted sugarcane juice is used to produce sugar or ethanol.
The fiber residue produced during the crushing process is bagasse.
Uses of Sugarcane Bagasse
Energy production: Used as boiler fuel in sugar mills to generate bioenergy.
Paper product manufacturing: used as raw material for paper and cardboard production.
Environmentally friendly packaging: used to produce degradable food packaging materials, such as disposable plates and lunch boxes.
How Does Sugarcane Fiber Compare To Other Packaging Alternatives?
Sugarcane fiber, derived from bagasse (the fibrous byproduct of sugarcane processing), stands out as an eco-friendly packaging alternative when compared to materials like plastic, paper, and other plant-based fibers.
1. Environmental Impact
Sugarcane Fiber: Fully biodegradable and compostable, breaking down into organic matter in a matter of weeks in industrial composting settings. Its production repurposes agricultural waste, reducing the need for virgin resources.
Plastic: Non-biodegradable, often ends up in landfills or oceans, contributing to long-term pollution and microplastic issues.
Paper: Renewable and compostable but requires significant water, energy, and chemicals for production, often leading to higher carbon emissions than sugarcane fiber.
Other Plant-Based Fibers (e.g., bamboo, wheat straw): Similar environmental benefits but may require more intensive processing compared to bagasse.
2. Performance
Sugarcane Fiber: Heat-resistant, grease-proof, and sturdy, making it suitable for hot or cold food applications. It maintains structural integrity better than many paper alternatives.Plastic: Highly durable and versatile but lacks eco-credentials.
Paper: Can weaken with exposure to moisture and heat, making it less ideal for certain food packaging uses.
Other Fibers: Typically durable but may lack the grease and heat resistance inherent to sugarcane-based products.
3. Cost
Sugarcane Fiber: Moderately priced; costs have been decreasing with advances in production technology but may still be higher than traditional plastic.
Plastic: Generally the cheapest due to established manufacturing infrastructure and economies of scale.
Paper: Similar or slightly higher cost than sugarcane fiber, depending on the type and processing. Other Fibers: Often more expensive due to less availability and higher production costs.
4. Aesthetic And Consumer Appeal
Sugarcane Fiber: Natural and earthy appearance, aligning with eco-conscious consumer preferences.
Plastic: Often viewed negatively due to environmental concerns, despite its practicality.
Paper: Commonly accepted but may lack the upscale look of sugarcane fiber.
Other Fibers: Unique textures can appeal to niche markets but are less common.
Qualifications
Explore our range of certifications that highlight our commitment to quality and sustainability.